CCNA 1 v7 Modules 4-7 Exam Answers: Learn the Key Concepts to Pass the Exam
This blog post provides comprehensive CCNA 1 v7 Modules 4-7 exam answers, covering all the key concepts in the exam. The answers are written by experienced CCNA certified professionals, and they are updated to the latest exam syllabus. By studying these answers, you can boost your chances of passing the CCNA 1 v7 exam with confidence.
CCNA 1 v7 Modules 4-7 Exam Answers: Ethernet Concepts – Our free guide offers everything you need to pass the CCNA 1 v7 Modules 4-7 exam.
NOTE: If you have a new question on this test, please comment Question and Multiple-Choice list in the form below this article. We’ll quickly refresh your access to the answers. I’m grateful. Your contribution to the website is greatly appreciated.

CCNA 1 v7 Modules 4-7 Exam Answers: Ethernet Concepts Exam Answers
You May Like:
Modules 1 – 3: Basic Network Connectivity and Communications Exam Answers
Modules 16 – 17: Building and Securing a Small Network Exam Answers
1. Why are two strands of fiber used for a single fiber optic connection?
- The two strands allow the data to travel for longer distances without degrading.
- They prevent crosstalk from causing interference on the connection.
- They allow for full-duplex connectivity.
- They increase the speed at which the data can travel.
2. What is the purpose of the OSI physical layer?
- controlling access to media
- transmitting bits across the local media
- performing error detection on received frames
- exchanging frames between nodes over physical network media
3. Which characteristic describes crosstalk?
- the distortion of the network signal from fluorescent lighting
- the weakening of the network signal over long cable lengths
- the distortion of the transmitted messages from signals carried in adjacent wires
- the loss of wireless signal over excessive distance from the access point
4. Match the situation with the appropriate use of network media.
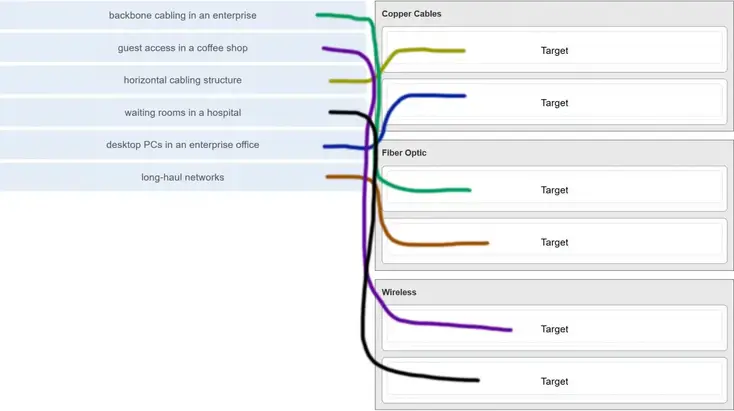
5. Which procedure is used to reduce the effect of crosstalk in copper cables?
- requiring proper grounding connections
- twisting opposing circuit wire pairs together
- wrapping the bundle of wires with metallic shielding
- designing a cable infrastructure to avoid crosstalk interference
- avoiding sharp bends during installation
6. What are two characteristics of fiber-optic cable? (Choose two.)
- Each pair of cables is wrapped in metallic foil.
- It is not affected by EMI or RFI.
- It combines the technique of cancellation, shielding, and twisting to protect data.
- It typically contains 4 pairs of fiber-optic wires.
- It is more expensive than UTP cabling is.
7. A network administrator is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical financial application. The administrator notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
8. What is a primary role of the Physical layer in transmitting data on the network?
- provide physical addressing to the devices
- create the signals that represent the bits in each frame on to the media
- determine the path packets take through the network
- control data access to the media
9. Refer to the graphic. What type of cabling is shown?

- STP
- UTP
- fiber
- coax
10. With the use of unshielded twisted-pair copper wire in a network, what causes crosstalk within the cable pairs?
- the use of braided wire to shield the adjacent wire pairs
- the magnetic field around the adjacent pairs of wire
- the reflection of the electrical wave back from the far end of the cable
- the collision caused by two nodes trying to use the media simultaneously
11. In addition to the cable length, what two factors could interfere with the communication carried over UTP cables? (Choose two.)
- bandwidth
- crosstalk
- size of the network
- electromagnetic interference
- signal modulation technique
12. Which two devices commonly affect wireless networks? (Choose two.)
- Blu-ray players
- cordless phones
- home theaters
- microwaves
- incandescent light bulbs
- external hard drives
13. Refer to the graphic. What type of cabling is shown?

- STP
- coax
- UTP
- fiber
14. Which two statements describe the services provided by the data link layer? (Choose two.)
- It defines the end-to-end delivery addressing scheme.
- It maintains the path between the source and destination devices during the data transmission.
- It manages the access of frames to the network media.
- It provides reliable delivery through link establishment and flow control.
- It packages various Layer 3 PDUs into a frame format that is compatible with the network interface.
- It ensures that application data will be transmitted according to the prioritization.
15. What is contained in the trailer of a data-link frame?
- logical address
- physical address
- error detection
- data
16. What is the function of the CRC value that is found in the FCS field of a frame?
- to verify the physical address in the frame
- to verify the integrity of the received frame
- to verify the logical address in the frame
- to compute the checksum header for the data field in the frame
17. Which statement describes a characteristic of the frame header fields of the data link layer?
- They all include the flow control and logical connection fields.
- They vary depending on protocols.
- Ethernet frame header fields contain Layer 3 source and destination addresses.
- They include information on user applications
18. A network team is comparing physical WAN topologies for connecting remote sites to a headquarters building. Which topology provides high availability and connects some, but not all, remote sites?
- mesh
- hub and spoke
- partial mesh
- point-to-point
19. What is the auto-MDIX feature?
- It enables a device to automatically configure the speed of its interface.
- It enables a device to automatically configure an interface to use straight-through or a crosover cable.
- It enables switch to dynamically select the forwarding method.
- It enables a device to automatically configure the duplex settings of a segment.
20. Which two devices commonly affect wireless networks? (Choose two.)
- external hard drives
- Blu-ray players
- microwaves
- incandescent light bulbs
- cordless phones
- home theaters
21. Which two fields or features does Ethernet examine to determine if a received frame is passed to the data link layer or discarded by the NIC? (Choose two.)
- auto-MDIX
- CEF
- minimum frame size
- Frame Check Sequence
- source MAC address
22. Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI data link layer? (Choose two.)
- Places information in the frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame.
- Integrates various physical technologies.
- Controls the NIC responsible for sending and receiving data on the physical medium.
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Communicates between the networking software at the upper layers and the device hardware at the lower layers.
23. Which media communication type does not require media arbitration in the data link layer?
- deterministic
- full-duplex
- half-duplex
- controlled access
24. What OSI physical layer term describes the process by which one wave modifies another wave?
- modulation
- IEEE
- EIA/TIA
- air
25. What OSI physical layer term describes the capacity at which a medium can carry data?
- IEEE
- EIA/TIA
- bandwidth
- air
26. Which statement describes an extended star topology?
- End devices are connected together by a bus and each bus connects to a central intermediate device.
- End devices connect to a central intermediate device, which in turn connects to other central intermediate devices.
- Each end system is connected to its respective neighbor via an intermediate device.
- All end and intermediate devices are connected in a chain to each other.
27. The “Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI data link layer? (Choose two.)” question has changed!
new questions:
- Enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same network interface and media
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Provides synchronization between source and target nodes.
- Integrates various physical technologies.
- Communicates between the networking software at the upper layers and the device hardware at the lower layers.
28 . What OSI physical layer term describes the measure of the transfer of bits across a medium over a given period of time?
- throughput
- bandwidth
- latency
- goodput
29. What OSI physical layer term describes the amount of time, including delays, for data to travel from one point to another?
- bandwidth
- throughput
- latency
- goodput
30. What is a characteristic of the LLC sublayer?
- It provides the logical addressing required that identifies the device.
- It places information in the frame allowing multiple Layer 3 protocols to use the same network interface and media.
- It provides delimitation of data according to the physical signaling requirements of the medium.
- It defines software processes that provide services to the physical layer.
31. What OSI physical layer term describes the amount of time, including delays, for data to travel from one point to another?
- latency
- fiber-optic cable
- air
- copper cable
32. What OSI physical layer term describes the measure of usable data transferred over a given period of time?
- goodput
- fiber-optic cable
- air
- copper cable
33. What are three ways that media access control is used in networking? (Choose three.)
- Ethernet utilizes CSMA/CD.
- Contention-based access is also known as deterministic.
- Media access control provides placement of data frames onto the media.
- 802.11 utilizes CSMA/CD.
- Data link layer protocols define the rules for access to different media.
- Networks with controlled access have reduced performance due to data collisions.
34. What OSI physical layer term describes the physical medium which uses electrical pulses?
- fiber-optic cable
- air
- copper cable
- goodput
35. During the encapsulation process, what occurs at the data link layer for a PC connected to an Ethernet network?
- An IP address is added.
- The physical address is added.
- The logical address is added.
- The process port number is added.
36. What OSI physical layer term describes the physical medium that uses the propagation of light?
- goodput
- fiber-optic cable
- latency
- throughput
37. What three items are contained in an Ethernet header and trailer? (Choose three.)
- source IP address
- destination IP address
- source MAC address
- destination MAC address
- error-checking information
38. What OSI physical layer term describes the physical medium for microwave transmissions?
- goodput
- air
- latency
- throughput
39. What type of communication rule would best describe CSMA/CD?
- flow control
- access method
- message encapsulation
- message encoding
40. Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI data link layer? (Choose two.)
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Controls the NIC responsible for sending and receiving data on the physical medium.
- Places information in the frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame.
- Implements a trailer to detect transmission errors.
- Enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same network interface and media.
Case 2:
- Enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same network interface and media.
- Provides synchronization between source and target nodes.
- Implements a trailer to detect transmission errors.
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Places information in the frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame.
Case 3:
- Communicates between the networking software at the upper layers and the device hardware at the lower layers.
- Provides synchronization between source and target nodes.
- Integrates various physical technologies.
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same network interface and media.
Case 4:
- Enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same network interface and media.
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Integrates various physical technologies.
- Communicates between the networking software at the upper layers and the device hardware at the lower layers.
- Provides synchronization between source and target nodes.
Case 5:
- Places information in the frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame.
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Integrates various physical technologies.
- Controls the NIC responsible for sending and receiving data on the physical medium.
- Communicates between the networking software at the upper layers and the device hardware at the lower layers.
Case 6:
- Controls the NIC responsible for sending and receiving data on the physical medium
- Provides a mechanism to allow multiple devices to communicate over a shared medium.
41. Which two functions are performed at the LLC sublayer of the OSI data link layer? (Choose two.)
- Places information in the frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame.
- Enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same network interface and media.
- Integrates various physical technologies.
- Implements a process to delimit fields within a Layer 2 frame.
- Controls the NIC responsible for sending and receiving data on the physical medium.
42. Which two functions are performed at the LLC sublayer of the OSI data link layer? (Choose two.)
- Places information in the frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame.
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Performs data encapsulation.
- Controls the NIC responsible for sending and receiving data on the physical medium.
- Integrates various physical technologies.
43. Which three basic parts are common to all frame types supported by the data link layer? (Choose three.)
- type field
- MTU size
- header
- data
- trailer
- CRC value
44. Which two functions are performed at the LLC sublayer of the OSI data link layer? (Choose two.)
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same network interface and media.
- Provides data link layer addressing.
- Implements a trailer to detect transmission errors.
- Provides synchronization between source and target nodes.
45. Which statement is true about the CSMA/CD access method that is used in Ethernet?
- When a device hears a carrier signal and transmits, a collision cannot occur.
- All network devices must listen before transmitting.
- A jamming signal causes only devices that caused the collision to execute a backoff algorithm.
- Devices involved in a collision get priority to transmit after the backoff period.
46. Which two functions are performed at the LLC sublayer of the OSI data link layer? (Choose two.)
- Enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same network interface and media.
- Integrates various physical technologies.
- Adds Layer 2 control information to network protocol data.
- Implements a trailer to detect transmission errors.
- Provides synchronization between source and target nodes.
47. What is the auto-MDIX feature on a switch?
- the automatic configuration of an interface for 10/100/1000 Mb/s operation
- the automatic configuration of full-duplex operation over a single Ethernet copper or optical cable
- the automatic configuration of an interface for a straight-through or a crossover Ethernet cable connection
- the ability to turn a switch interface on or off accordingly if an active connection is detected
48. What action will occur if a switch receives a frame with the destination MAC address FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF?
- The switch shares the MAC address table entry with any connected switches.
- The switch forwards it out all ports except the ingress port.
- The switch does not forward the frame.
- The switch sends the frame to a connected router because the destination MAC address is not local.
49. What action will occur if a switch receives a frame with the destination MAC address 01:00:5E:00:00:D9?
- The switch does not forward the frame.
- The switch forwards it out all ports except the ingress port.
- The switch sends the frame to a connected router because the destination MAC address is not local.
- The switch shares the MAC address table entry with any connected switches.
50. What action will occur if a host receives a frame with a destination MAC address of FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF?
- The host forwards the frame to the router.
- The host will process the frame.
- The host sends the frame to the switch to update the MAC address table.
- The host forwards the frame to all other hosts.
51. What action will occur if a host receives a frame with a destination MAC address of FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF?
- The host returns the frame to the switch.
- The host will process the frame.
- The host replies to the switch with its own IP address.
- The host forwards the frame to all other hosts.
52. What action will occur if a switch receives a frame and does have the source MAC address in the MAC table?
- The switch adds it to its MAC address table associated with the port number.
- The switch refreshes the timer on that entry.
- The switch forwards the frame to the associated port.
- The switch sends the frame to a connected router because the destination MAC address is not local.
53. Which type of UTP cable is used to connect a PC to a switch port?
- console
- rollover
- straight-through
- crossover
54. What action will occur if a host receives a frame with a destination MAC address it does not recognize?
- The host replies to the switch with its own IP address.
- The host will discard the frame.
- The host forwards the frame to all other hosts.
- The host returns the frame to the switch.
55. Refer to the exhibit. What is the destination MAC address of the Ethernet frame as it leaves the web server if the final destination is PC1?
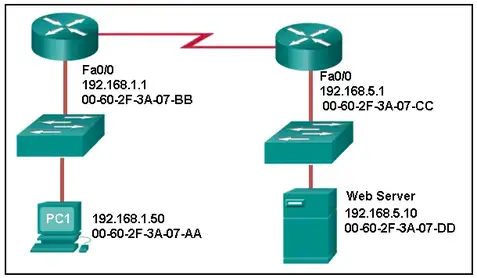
- 00-60-2F-3A-07-AA
- 00-60-2F-3A-07-CC
- 00-60-2F-3A-07-BB
- 00-60-2F-3A-07-DD
56. What are two examples of the cut-through switching method? (Choose two.)
- store-and-forward switching
- fast-forward switching
- CRC switching
- fragment-free switching
- QOS switching
57. A Layer 2 switch is used to switch incoming frames from a 1000BASE-T port to a port connected to a 100Base-T network. Which method of memory buffering would work best for this task?
- port-based buffering
- level 1 cache buffering
- shared memory buffering
- fixed configuration buffering
58. Which is a multicast MAC address?
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
- 5C-26-0A-4B-19-3E
- 01-00-5E-00-00-03
- 00-26-0F-4B-00-3E
59. Which frame forwarding method receives the entire frame and performs a CRC check to detect errors before forwarding the frame?
- cut-through switching
- store-and-forward switching
- fragment-free switching
- fast-forward switching
60. Refer to the exhibit. What is wrong with the displayed termination?

- The woven copper braid should not have been removed.
- The wrong type of connector is being used.
- The untwisted length of each wire is too long.
- The wires are too thick for the connector that is used.
61. What is one advantage of using the cut-through switching method instead of the store-and-forward switching method?
- has a positive impact on bandwidth by dropping most of the invalid frames
- makes a fast forwarding decision based on the source MAC address of the frame
- has a lower latency appropriate for high-performance computing applications
- provides the flexibility to support any mix of Ethernet speeds
62. Refer to the exhibit. The PC is connected to the console port of the switch. All the other connections are made through FastEthernet links. Which types of UTP cables can be used to connect the devices?
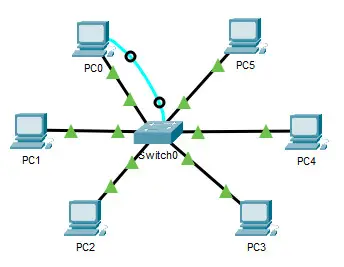
1 - rollover, 2 - crossover, 3 - straight-through 1 - rollover, 2 - straight-through, 3 - crossover 1 - crossover, 2 - rollover, 3 - straight-through 1 - crossover, 2 - straight-through, 3 - rollover
63. What is the purpose of the FCS field in a frame?
- to obtain the MAC address of the sending node
- to verify the logical address of the sending node
- to compute the CRC header for the data field
- to determine if errors occurred in the transmission and reception
64. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
65. Which port does Switch0 use to send frames to the host with the IPv4 address 10.1.1.5?
- Fa0/1
- Fa0/5
- Fa0/11
- Fa0/9
66. Which switching method has the lowest level of latency?
- cut-through
- store-and-forward
- fragment-free
- fast-forward
67. What does the term “attenuation” mean in data communication?
- time for a signal to reach its destination
- loss of signal strength as distance increases
- leakage of signals from one cable pair to another
- strengthening of a signal by a networking device
68. What is the auto-MDIX feature?
- It enables a device to automatically configure the duplex settings of a segment.
- It enables a device to automatically configure an interface to use a straight-through or a crossover cable.
- It enables a device to automatically configure the speed of its interface.
- It enables a switch to dynamically select the forwarding method.
69. What makes fiber preferable to copper cabling for interconnecting buildings? (Choose three.)
- lower installation cost
- greater distances per cable run
- limited susceptibility to EMI/RFI
- durable connections
- greater bandwidth potential
- easily terminated
70. A network administrator is connecting two modern switches using a straight-through cable. The switches are new and have never been configured. Which three statements are correct about the final result of the connection? (Choose three.)
- The link between the switches will work at the fastest speed that is supported by both switches.
- The link between switches will work as full-duplex.
- The auto-MDIX feature will configure the interfaces eliminating the need for a crossover cable.
- If both switches support different speeds, they will each work at their own fastest speed.
- The connection will not be possible unless the administrator changes the cable to a crossover cable.
- The duplex capability has to be manually configured because it cannot be negotiated.
71. Which two statements describe features or functions of the logical link control sublayer in Ethernet standards? (Choose two.)
- Logical link control is specified in the IEEE 802.3 standard.
- Logical link control is implemented in software.
- The LLC sublayer adds a header and a trailer to the data.
- The data link layer uses LLC to communicate with the upper layers of the protocol suite.
- The LLC sublayer is responsible for the placement and retrieval of frames on and off the media.
72. Which advantage does the store-and-forward switching method have compared with the cut-through switching method?
- collision detecting
- faster frame forwarding
- frame error checking
- frame forwarding using IPv4 Layer 3 and 4 information
73. What are two actions performed by a Cisco switch? (Choose two.)
- building a routing table that is based on the first IP address in the frame header
- forwarding frames with unknown destination IP addresses to the default gateway
- using the source MAC addresses of frames to build and maintain a MAC address table
- utilizing the MAC address table to forward frames via the destination MAC address
- examining the destination MAC address to add new entries to the MAC address table
74. When the store-and-forward method of switching is in use, what part of the Ethernet frame is used to perform an error check?
- source MAC address in the header
- CRC in the trailer
- destination MAC address in the header
- protocol type in the header
75. Which switching method uses the CRC value in a frame?
- cut-through
- fast-forward
- store-and-forward
- fragment-free